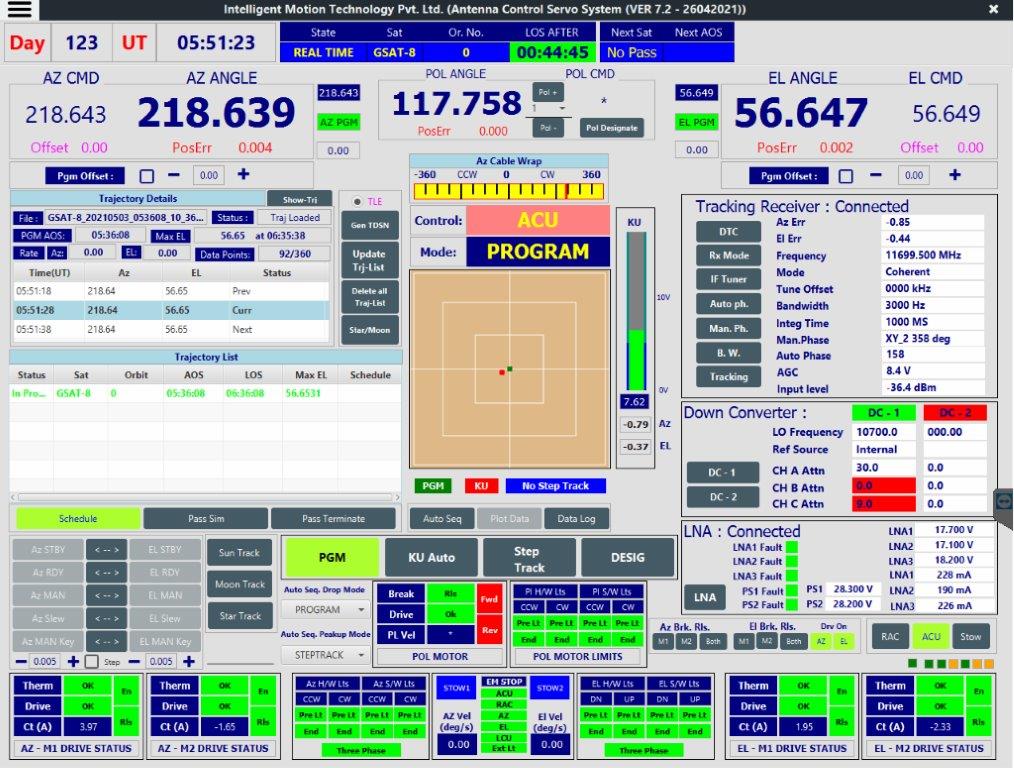
Antenna Control Servo System
Antenna Control Servo System
- At IMTPL, we conceptualize, integrate and deliver hi-tech limited and full motion servo systems for remote sensing, telemetry, data link and TTC communication requirements.
- We have provided numerous servo systems for Antennas of – 4.6m to 11m dish
- From 2Ghz (S-band) till 40Ghz (Ka band)
- Customizable to suit LEO, MEO and GEO satellite tracking
- Seamless integration for auto tracking based on different feeds
- Hi-performance servo control using Adaptive control algorithm
- Customizable UI along with Advanced monitoring and control software
Scope
- Operating Software
- Servo Motors & Drives, Motion Controls
- Electrical Panel
- Proving, Installation and Commissioning
- Documentation
- Test and Evaluation (T & E)
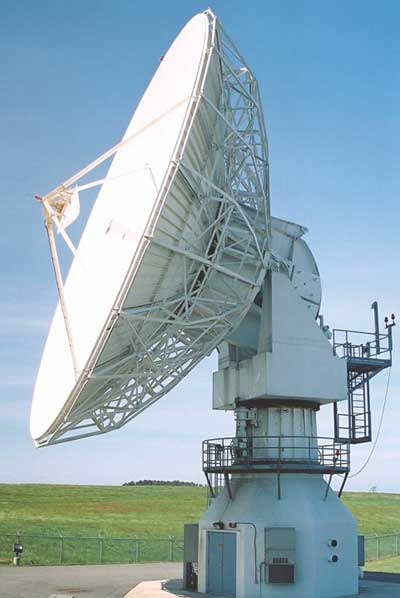

Application :
- ACSS is a high performance Servo System for tracking of Low Earth Orbit Satellites, Geo Synchronous Earth Orbit Satellites, Sun & Stars. ACSS is developed for precise motion control of the parabolic reflector type antennas using the state-of-the-art technology for modern digital control systems. Precise motion control is achieved by backlash removal in large gearboxes used with azimuth & elevation axis of antenna through usage of Dual Drive Counter Torque technique.
- Implementation of cascade control for closing the loop using signal being received from satellite with the help of high performance servo-motion controls & high resolution absolute encoders.
- ACSS has different operating modes like Standby, Manual, Slew, Designate, Program Track, Step Track, Monopulse Auto Track, Auto Sequence, Computer Designate Mode, Slave & Stow.
- We have several installation of ACSS to Space Programs of Satellite Research Organization of India & overseas.
Overview
- For tracking Stable or inclined GEO / MEO / LEO satellites, Launch Vehicles, Sun and Stars
- S, C, Ku or multiband operation
- Pointing, Step Track, Orbit Predictive Track, Monopulse systems
- Fixed or transportable earth stations
- Accommodates AZ / EL mounts with optional Polarizer
- Dual servo motor operation for each axis with counter torque for removal of backlash effect
- Optional timing interfaces – Network Time Protocol or mod code IRIG-B / EIA with count up / count down options
- Operations in local and remote modes
- Trajectory generation from NORAD two line elements
- Trajectory generation from orbital elements
- Data logging and plotting
- Usage of Precision Motion Controller
- High Performance Servo Drives
- High Resolution Absolute Encoders
Operating Modes:
- Standby-Brakes are applied and drives are disabled
- Manual– Axes movements are geared electronically with handwheels
- Slew-Slewing movements at variable speeds
- Designate– Axes move to destination angles at required velocities
- Program Track– Axes move as per the predicted trajectory and timeline
- Step Track– Axes move in successive small steps to maximize AGC
- Monopulse Auto Track– Axes are moved so as to make the tracking errors zero
- Auto Sequence– Automatic changeover from Program track to Monopulse auto track
- Computer Designate Mode– Axes are moved to follow the angle data continuously being received over the data link
- Slave– Axes are moved to follow the movement of co-located antenna
- Stow– Movement of the stow pins is made in this mode